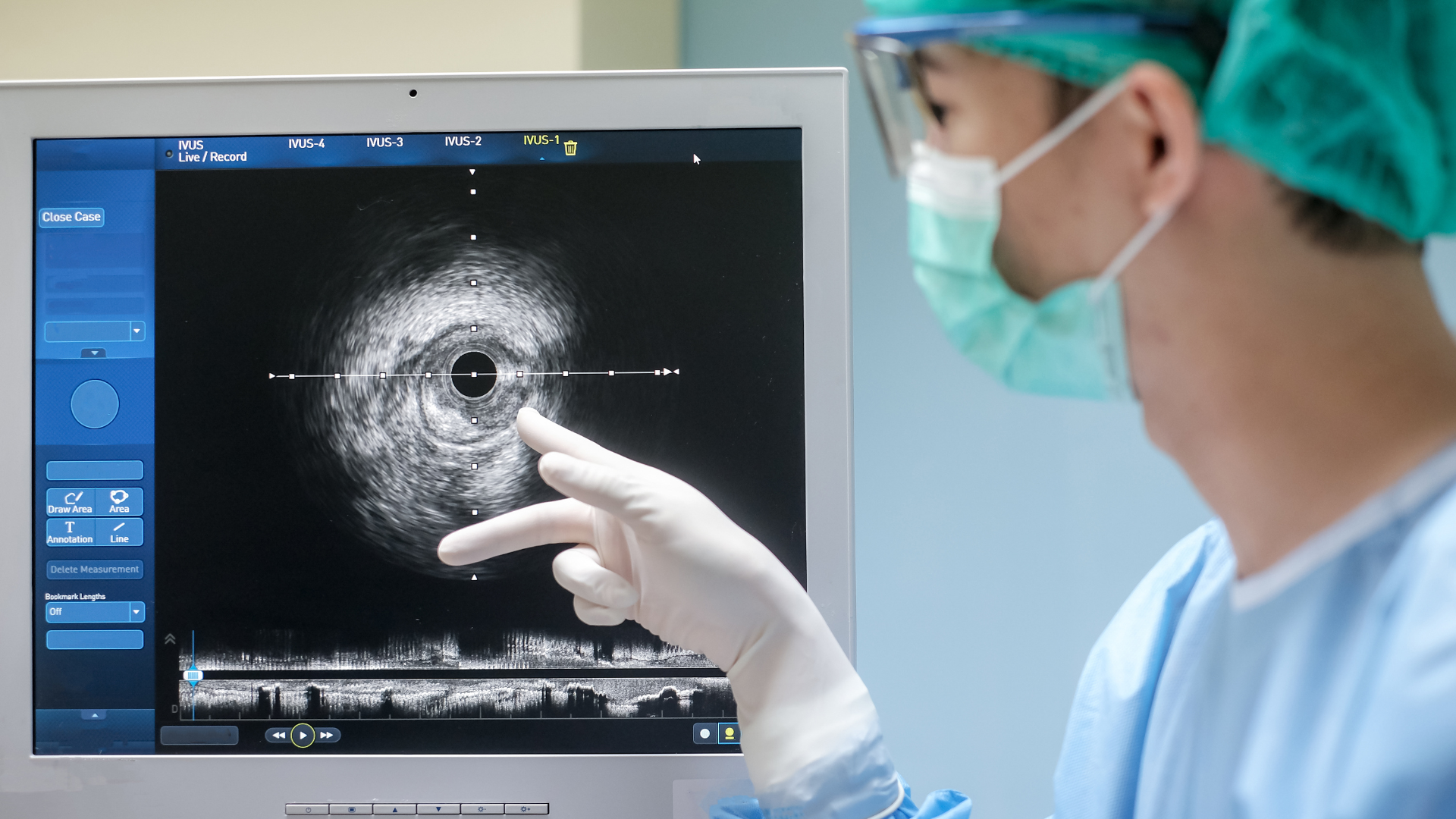
Catheterization: A Window into the Heart
Catheterization is a medical procedure that involves the insertion of a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into the body. While the term can encompass various applications, it is most commonly associated with cardiac catheterization, a diagnostic and interventional tool for evaluating and treating heart conditions.
At the heart of this procedure lies advanced imaging technology. Fluoroscopy, a continuous X-ray imaging technique, provides real-time visualization of the catheter’s journey through the blood vessels. This allows physicians to navigate the catheter with precision, reaching the target area for diagnosis or treatment. Contrast agents, such as iodine-based dyes, are often injected to enhance the visibility of blood vessels and heart chambers.
Cardiac catheterization is indispensable for diagnosing a myriad of heart conditions. It can reveal blockages in the coronary arteries, the vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle. This information is crucial for identifying coronary artery disease, a leading cause of heart attacks. Additionally, catheterization can assess heart valve function, detect congenital heart defects, and evaluate the heart’s pumping ability. Beyond diagnosis, catheterization is a cornerstone of interventional cardiology. Procedures like angioplasty, where a balloon is inflated to open blocked arteries, and stent placement, which acts as a scaffold to keep arteries open, are performed through catheter-based techniques. These interventions have revolutionized the treatment of heart disease, reducing the need for open-heart surgery in many cases.
The importance of catheterization cannot be overstated. It offers a minimally invasive approach to diagnosing and treating a wide range of heart conditions. Early detection and timely intervention through catheterization can significantly improve patient outcomes, reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular complications. Moreover, catheterization has contributed to enhanced patient quality of life by enabling effective management of heart disease and reducing the need for extensive surgical procedures. As technology continues to advance, catheterization is poised to play an even more critical role in cardiac care, offering hope and improved outcomes for countless patients.
While the procedure is generally safe, it carries inherent risks, such as bleeding, allergic reactions to contrast agents, and irregular heart rhythms. However, these risks are typically low and are carefully managed by skilled healthcare professionals.
For modern medical professionals, catheterization is a sophisticated diagnostic and therapeutic tool that has transformed the landscape of cardiology. Its ability to provide detailed insights into heart function and structure, coupled with its potential for minimally invasive treatments, has made it an invaluable asset in the fight against heart disease.



Leave a Reply